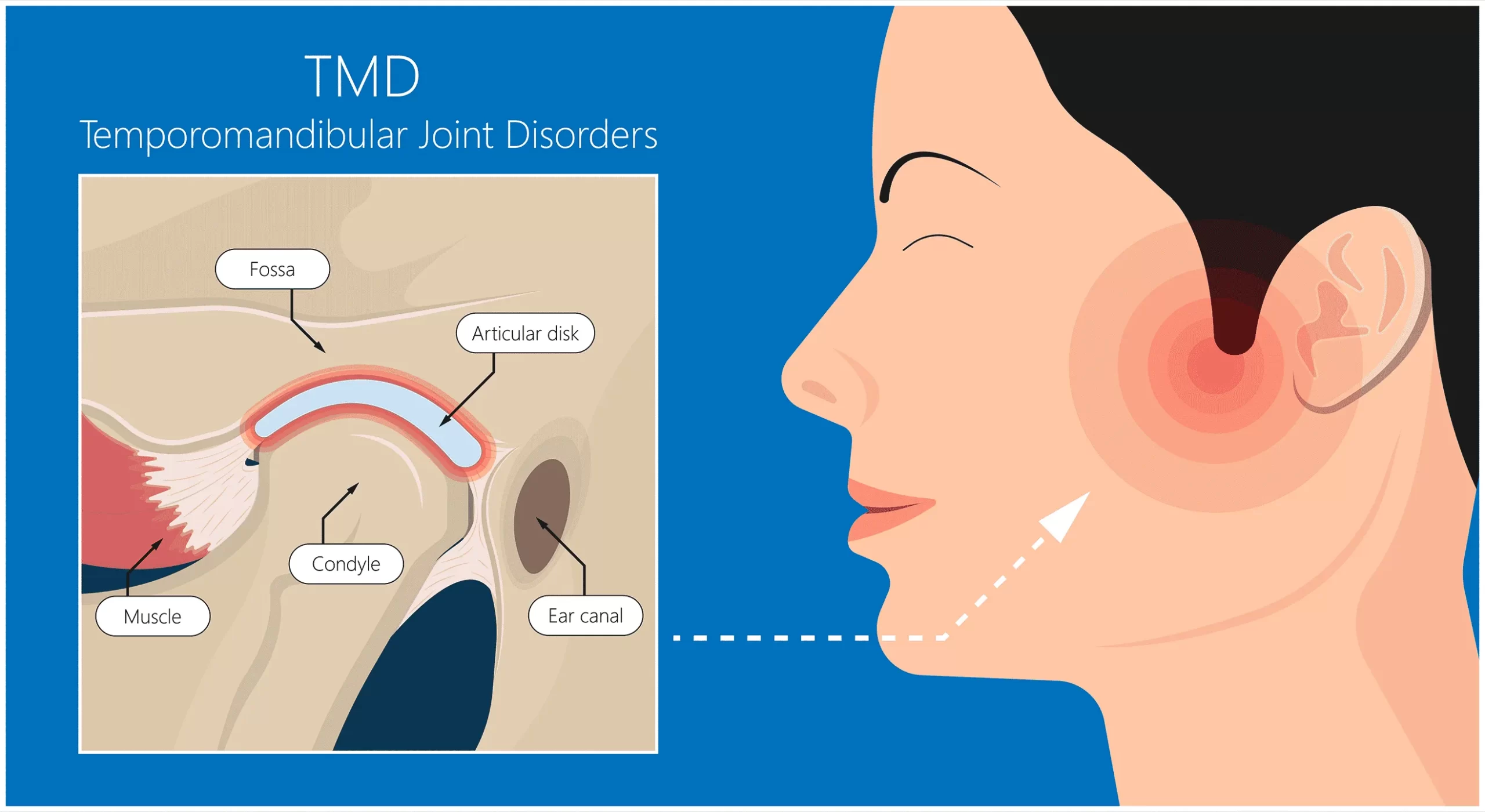
Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD) refer to a group of conditions that affect the jaw joint, muscles, and surrounding structures. These disorders can cause pain, restricted movement, and discomfort in the jaw area, often impacting essential daily activities such as eating, speaking, and even yawning. While mild cases may resolve on their own, chronic or severe TMD can significantly reduce one’s quality of life if left untreated.
If you are experiencing persistent jaw discomfort or clicking sounds while moving your mouth, it may be beneficial to seek professional evaluation for Tmd. Specialists can assess the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatment options to help restore normal jaw function and alleviate pain.
Understanding TMD and Its Impact on Jaw Function
TMD primarily affects the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jawbone to the skull. This joint allows for smooth movement when talking, chewing, or swallowing. When the joint becomes inflamed, misaligned, or strained, it can lead to pain and difficulty in movement—hallmarks of TMD.
In many cases, TMD is caused by a combination of factors such as jaw injury, stress-related clenching or grinding, arthritis, or misalignment of the teeth and jaw. Since the TMJ is one of the most used joints in the body, even minor irritation can cause noticeable discomfort and functional limitations.
Common Symptoms of TMD
People suffering from TMD may experience a range of symptoms that vary in intensity. Some of the most common include:
- Pain or tenderness in the jaw joint area
- Clicking, popping, or grating sounds when moving the jaw
- Limited ability to open or close the mouth fully
- Facial pain or headaches
- Earaches or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Stiffness or fatigue in the jaw muscles
In severe cases, TMD can cause the jaw to lock in an open or closed position, making it difficult to move without discomfort.
How TMD Disrupts Jaw Function
The temporomandibular joint is designed to move both smoothly and powerfully, allowing for complex motions like chewing and speaking. When TMD occurs, inflammation or misalignment interferes with this motion, resulting in uneven pressure on the joint.
Muscle tension, often due to clenching or grinding, can also restrict movement and cause pain to radiate across the face, neck, and shoulders. This dysfunction not only limits mobility but may also alter how the upper and lower teeth fit together, creating further discomfort.
If left untreated, chronic TMD can lead to long-term joint damage or degeneration, emphasizing the importance of timely diagnosis and management.
Effective Ways to Manage TMD
1. Self-Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Mild cases of TMD can often be managed with simple home remedies. Applying warm compresses to the jaw area can help relax tight muscles and reduce pain. Avoiding hard or chewy foods, limiting jaw movements like wide yawning, and practicing good posture can also ease pressure on the joint.
2. Stress Reduction
Stress is a major contributor to jaw tension and teeth grinding. Relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises can help minimize stress-related habits that aggravate TMD.
3. Jaw Exercises
A dentist or physical therapist may recommend gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to improve flexibility and restore smooth jaw motion. Regularly performing these exercises can enhance joint function and reduce stiffness over time.
4. Medication
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can relieve pain and swelling. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe muscle relaxants or corticosteroid injections to manage inflammation and discomfort.
5. Oral Appliances
Custom-made mouthguards or splints are often used to prevent teeth grinding and reduce jaw strain during sleep. These devices help reposition the jaw and distribute pressure more evenly, providing long-term relief.
6. Professional Treatment Options
For persistent TMD symptoms, dental professionals may recommend advanced treatments such as physiotherapy, ultrasound therapy, or bite correction procedures. In rare and extreme cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joint components.
When to Seek Professional Help
You should consult a dental or TMJ specialist if you experience persistent jaw pain, difficulty opening your mouth, or continuous clicking sounds in your jaw. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve your chances of full recovery.
During your visit, your dentist may perform a physical examination, take imaging scans, or review your bite alignment to determine the best treatment plan.
Conclusion
TMD is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact daily life if not managed properly. By understanding its causes and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their jaw health. With proper care, lifestyle adjustments, and professional treatment, most people can find relief from pain and regain full jaw function.
Early diagnosis and consistent management are key to preventing long-term discomfort and maintaining healthy joint movement.